What Is Genetics?
Genetics is the study of genes. Our genes carry information that gets passed from one generation to the next. For example, genes are why one child has blonde hair like their mother, while their sibling has brown hair like their father. Genes also determine why some illnesses run in families and whether babies will be male or female.
What Are Genes?
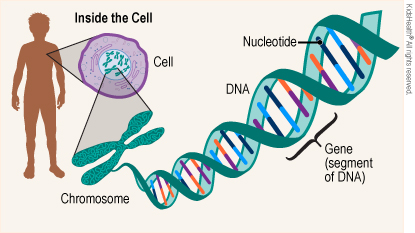
Genes are sections of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) that are found inside every human cell. They’re so tiny that they can be seen only under a powerful microscope. DNA is made of four chemicals that form pairs in different combinations. The combinations create codes for different genes. Each person has about 20,000 genes. The genes code for different traits, such as eye color, body type, or male or female sex.
What Is a Chromosome?
Inside each cell, DNA is tightly wrapped together in structures called chromosomes. Every normal cell has 23 pairs of chromosomes (for a total of 46):
- 22 pairs of chromosomes are the same in males and females. These are called autosomes (AW-tuh-soamz).
- The 23rd pair — the sex chromosomes — determines the sex of the baby. Females have two X chromosomes and males have one X chromosome and one Y chromosome.
How Do Genes Pass From Parent to Child?
To form a fetus, an egg from the mother and sperm from the father come together. The egg and sperm each have one half of a set of chromosomes. The egg and sperm together give the baby the full set of chromosomes. So, half the baby’s DNA comes from the mother and half comes from the father.
What Is a Genetic Disorder?
A genetic disorder happens when a gene (or genes) has a problem with its code, and this causes a health problem. Sometimes a genetic disorder happens when a child inherits it from one or both parents. Other times, it happens only in the child (and the parents do not have the genetic disorder).
How Do Genetic Disorders Happen?
Different things can cause a genetic disorder, such as:
- a change (mutation) in one gene on a
- a missing part of a chromosome (called a deletion)
- genes shifting from one chromosome to another (called a translocation)
- an extra or missing chromosome
- too few or too many sex chromosomes
Looking Ahead
Scientists are learning more and more about genetics. A worldwide research project called The Human Genome Project created a map of all human genes. It shows where the genes are located on the chromosomes. Doctors can use this map to find and treat or cure some kinds of genetic disorders. There is hope that treatments for many genetic disorders will be developed in the future.


