What Are Antibiotics?
Antibiotics are medicines that treat infections caused by bacteria, a type of germ. Some bacteria are good for our bodies, but others cause illness. Bacterial infections happen when harmful bacteria enter the body and multiply.
How Do Antibiotics Work?
Antibiotic (an-ty-by-AH-tik) medicines treat infections by killing bacteria or stopping them from growing and multiplying. Bacteria are different from other kinds of germs (like viruses and fungi). Antibiotics are effective only against bacteria. That means they won’t work against illnesses like colds or the flu.
What Are the Types of Antibiotics?
Antibiotics come in different forms. Doctors might prescribe them as:
- liquids or pills that are swallowed
- topical creams (applied to skin). Many of these are also available without a prescription at drugstores and superstores.
- injections (shots) given directly into the muscle
- a special liquid form put into an IV line (into a vein). IV antibiotics are usually given (or at least started) in the hospital. Kids can also safely get IV treatment at home.
What Problems Can Antibiotics Treat?
Many infections and other problems caused by bacteria can be treated with antibiotics, including:
- skin infections like impetigo and abscesses
- severe acne
- Lyme disease
- bacterial pneumonia
- strep throat
- sinus infections caused by bacteria
- urinary tract infections (UTIs)
- some ear infections
- sexually transmitted infections, like chlamydia, syphilis, and gonorrhea
How Should I Give My Child an Antibiotic?
If your child needs an antibiotic:
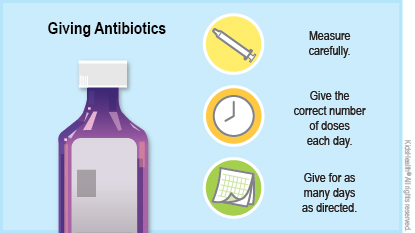
Follow the doctor’s directions. Make sure to give the right amount at the right times.
Know how to give the medicine. Check the label if you aren’t sure. Some antibiotics might have special directions for use, such as taking them on an empty stomach, with a meal, or with lots of water. While on some kinds of antibiotics, kids might need to limit their sun exposure or stop taking other kinds of medicine.
Give all the doses. Your child should take all doses of the medicine as directed, even if they start to feel better. This is the best way to kill the harmful bacteria. If they stop taking the antibiotics early, the infection may not be fully treated and may come back and be harder to treat.
Store the medicine carefully. Some antibiotics need to be in the refrigerator. Hot temperatures can affect antibiotics, so don’t keep them in hot places like your car. If you have questions about how to store the medicine, check the label or talk to the pharmacist. Keep all medicines out of reach of young children.
Follow up when your child is done taking the medicine. The doctor might want to see your child after they’re done taking the antibiotics to make sure the infection is gone.
What Do Antibiotic Overuse and Resistant Bacteria Mean?
Antibiotic overuse is when antibiotics are used when they're not needed. Overprescribing of antibiotics has led to resistant bacteria. These germs are harder to treat because they no longer respond as well to antibiotic treatment. Some bacteria are now resistant to even the most powerful antibiotics.
What Can Help Prevent Antibiotic Overuse and Resistant Bacteria?
Doctors prescribe antibiotics only for infections they think the drugs will help treat. It can be tempting to ask your doctor for antibiotics when your child is sick. But they won’t help when an illness is likely due to a virus. Instead, talk to the doctor about ways to treat the symptoms to help your child feel better.
If your doctor does prescribe antibiotics:
- Give your child the antibiotics exactly as prescribed. They should not stop taking them early, even if they feel better.
- Only give your child the antibiotics prescribed for them for that infection.
- Don’t give antibiotics prescribed for your child to someone else.
- Don’t save leftover doses for “next time.” Doctors pick an antibiotic very carefully to treat each bacterial infection. So antibiotics for one infection might not work against another infection caused by different bacteria. Throw out leftover antibiotics or get rid of them through a medicine take-back program in your community. Talk to your pharmacist if you need help.
What Side Effects Can Antibiotics Cause?
Antibiotics can cause such side effects as diarrhea, nausea, dizziness, a rash, and yeast infections. Most side effects usually are mild and stop when a person is done taking the medicine. Check with your doctor, though, if your child has a rash or a yeast infection. A rash could be just a side effect that will go away or could be a sign of an allergy. A yeast infection might need treatment to get better.
If your child has an upset stomach or diarrhea while taking antibiotics, ask the doctor if they should take probiotics. Probiotics are "good" bacteria that help keep the intestines healthy. Also, when antibiotics kill the “good” bacteria in the intestines, bacteria called Clostridioides difficile (C diff., for short) can overgrow and cause an infection. This can cause diarrhea and other problems and needs treatment to get better.
When Should I Call the Doctor?
Call the doctor if your child is on an antibiotic and:
- doesn't start to feel better or still has a fever within 48 hours of starting the antibiotic
- has stomach pain, nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea
- has blood in the poop
- has trouble taking the antibiotic
- develops a new rash
- seems to be getting worse
Go to the ER if your child:
- has trouble breathing
- has trouble swallowing
- has swelling of the throat or tongue
Rarely, an infection can get much worse, leading to a medical emergency called sepsis. You know your child best. Call the doctor or get medical help right away if your child is sick and not getting better, seems sicker than usual to you, or has an infection that's not getting better or gets worse.
What Else Should I Know?
Besides treating bacterial infections, antibiotics sometimes are used to prevent them. A child who gets a lot of UTIs, for example, might take a small dose of antibiotics to make them less likely to come back.
Doctors also might give “prophylactic” antibiotics to patients before an operation to help prevent skin infections around the surgical area.


