What Is Roseola?
Roseola (roe-zee-OH-lah) is a viral illness that most commonly affects kids between 6 months and 2 years old. It's also known as sixth disease, exanthem subitum, and roseola infantum.
It is usually marked by several days of high fever, followed by a distinctive rash just as the fever breaks.
What Are the Signs & Symptoms of Roseola?
Most children with roseola develop a high fever (often higher than 103°F or 39.5°C) that usually lasts 3–5 days. During this time, a child might be fussy or irritable, not eat as much as usual, and may have a sore throat and swollen lymph nodes (glands) in the neck. They also may have mild respiratory symptoms (like a runny nose or cough) or gastrointestinal symptoms (like diarrhea or vomiting).
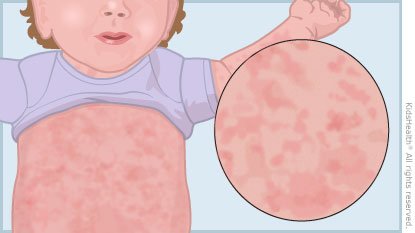
The high fever often ends suddenly, and at about the same time a rash starts on the trunk before spreading to the neck, face, arms, or legs. On light skin, the rash can look like pink or red spots. On darker skin, it might be harder to see. It’s usually not itchy.
The fast-rising fever can trigger febrile seizures (convulsions caused by high fevers) in about 10% to 15% of young children who have roseola. Signs of a febrile seizure include:
- unconsciousness
- 2 to 3 minutes of jerking or twitching in the arms, legs, or face
- loss of control of the bladder or bowels
What Causes Roseola?
Two common, closely related viruses can cause roseola: human herpesvirus (HHV) type 6 and type 7. These viruses belong to the same family as the better-known herpes simplex viruses (HSV), but do not cause the cold sores and genital herpes infections that HSV can cause.
Is Roseola Contagious?
Roseola is contagious. The infection spreads when a child with roseola talks, sneezes, or coughs, sending tiny droplets into the air that others can breathe in. The droplets also can land on surfaces; if other children touch those surfaces and then their nose or mouth, they can become infected.
Roseola is most contagious during the fever phase. After the fever goes down and the rash breaks out, a child can return to childcare or preschool.
The virus also can be spread by people who have no symptoms, because it stays in the body after they're infected.
Can Roseola Be Prevented?
There is no known way to prevent roseola. But because it affects young kids rather than adults, it's thought that a bout of roseola in childhood may provide some lasting immunity to the illness. Repeat cases of roseola can happen, but are not common.
How Long Does Roseola Last?
The fever of roseola lasts from 3 to 5 days, followed by a rash lasting from hours to a few days.
How Is Roseola Diagnosed?
To make a diagnosis, a doctor will take a and do an exam. A diagnosis of roseola is often uncertain until the fever drops and the rash appears. So the doctor may order tests to make sure that another infection isn't causing the fever.
How Is Roseola Treated?
Roseola usually doesn't need medical care. When it does, most treatment focuses on easing symptoms. Antibiotics can't treat roseola because viruses cause it, not bacteria.
Home Care
Acetaminophen (such as Tylenol) or ibuprofen (such as Advil or Motrin) can help to ease a fever if it's making a child uncomfortable. Never give aspirin to a child who has a viral illness because such use is linked to Reye syndrome, which can lead to liver failure and death.
While some parents use lukewarm sponge baths to lower fever, there is no proof that this really works. In fact, sponge baths can make children uncomfortable. Never give your child an icy or cold bath or alcohol rubs.
To prevent dehydration from the fever, encourage your child to drink plenty of fluids, such as breast milk, formula, and oral rehydration solution (Pedialyte, Enfalyte, or a store brand). You also can give water, soup, or flavored gelatin. For a sore throat, cold or frozen liquids (such as ice pops) can be soothing.
When Should I Call the Doctor?
Call the doctor if your child seems weak or less active than usual or won't drink or breastfeed. If your child has a seizure, get emergency care right away.


